What Is Chelation Therapy?
Chelation therapy is a treatment designed to remove harmful minerals and waste products from the body. It is administered via intravenous infusion using a specific medication known as a chelating agent.
The word “chelation” originates from the Greek word chele, meaning “claw,” referencing how the agent “grabs onto” heavy metals in the body—much like a crab claw—and binds with them for elimination. Once infused, the chelating agent forms complexes with these toxic metals, allowing them to be safely excreted from the body.
In the United States, chelation therapy has been practiced for over 50 years as a clinically recognized treatment, particularly for improving arterial health and preventing conditions such as strokes and heart attacks.
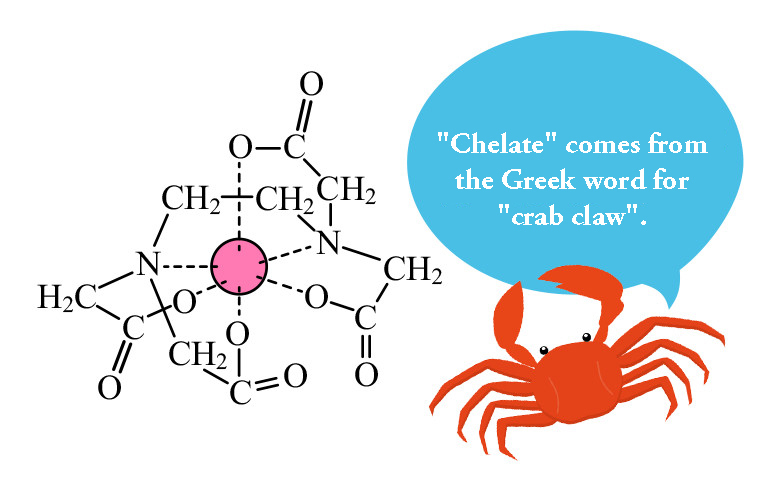
(Chelate/Coordination Compound)
Also known as a coordination compound, this model illustrates how ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) forms a chelate complex by binding with a calcium ion.
Clinical Benefits of Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy has been the subject of numerous clinical studies, with many reports supporting its efficacy. In Japan, chelation infusions have been used since the 1940s—originally as a treatment for lead poisoning among miners and painters exposed to lead-based pigments.
While it was initially reserved for treating heavy metal toxicity, recent years have seen a growing body of international research—especially from the U.S. and Europe—highlighting its potential to address a broader range of diseases and symptoms. Today, chelation therapy is gaining recognition as a valuable anti-aging and vascular care treatment.
Its potential benefits include improved cardiovascular health, reduced oxidative stress, and enhanced circulation, making it a promising addition to aging care protocols.
Reported Improvements with Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy has been associated with positive outcomes in a wide range of conditions, including: ・Atherosclerosis ・Coronary artery disease (e.g., angina, myocardial infarction) ・Peripheral vascular disease ・Arthritis and multiple sclerosis ・Parkinson’s disease ・Stroke and Alzheimer’s disease ・Sensory impairments (vision, hearing, smell) ・Development of collateral circulation ・Decreased blood viscosity ・Enhanced function of cell membranes and intracellular organelles ・Reduced arterial spasms ・Lower free radical production ・Slowed progression of aging ・Healing of tissue necrosis ・Improved skin pigmentation ・Healing of diabetic ulcers ・Improved muscular function ・Restoration of vitality
Recommended Frequency of Chelation Therapy
| For aging care (general wellness) | 10 sessions (once every 1–2 weeks) followed by maintenance every 3 to 6 months |
|---|---|
| For prevention of atherosclerosis (e.g., heart attack, stroke) | 10 sessions (once every 1–2 weeks) followed by maintenance every 3 to 6 months |
| For treatment of atherosclerosis (asymptomatic) | 20 sessions (once every 1–2 weeks) |
| For treatment of atherosclerosis (symptomatic) | 30 sessions (once every 1–2 weeks) |
| For removal of toxic heavy metals | 20 sessions (once every 1–2 weeks) |
| For ongoing maintenance therapy | Once every 3 to 6 months |
Safety and Side Effects of Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy is considered to be an extremely safe treatment. In the United States, over 20 million sessions have been conducted on more than one million individuals without any serious adverse events.
(Source)A Textbook on EDTA Chelation Therapy: Second Edition 2001
Minor side effects such as mild vascular discomfort, headaches, or fatigue may occasionally occur, but these can be effectively managed under medical supervision by adjusting the frequency or dosage as needed. Responses vary from person to person—some may notice detoxification effects even in the early stages of treatment.
Chelation Therapy Around the World

Chelation therapy has been widely practiced in the United States for over 50 years and is regarded as a reliable and evidence-based form of complementary medicine for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disease, and stroke.
In a country like the U.S., where myocardial infarction remains a leading cause of death, there is significant interest in this therapy. A clinical study involving 24,000 cases reported clinical improvement in 88% of heart disease patients treated with chelation therapy (Cappell LT. J Adv Med, 1993).
Moreover, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) launched a large-scale clinical trial in April 2003 to evaluate chelation therapy’s efficacy in treating coronary artery disease. The results, published later, demonstrated its therapeutic potential.
Going forward, chelation therapy is expected to become a key modality not only in the U.S. but globally—as a central pillar in both cardiovascular disease prevention and advanced aging care.
ation Therapy at Kita-Aoyama D.CLINIC: Treatment Flow
Below is an outline of the treatment process:
1. Initial Testing
We perform diagnostic tests to evaluate the degree of arteriosclerosis,
oxidative stress, and other relevant factors. (Optional, upon request)
2. Medical Consultation
Based on your current symptoms and overall health condition,
we will discuss your concerns and create an appropriate treatment plan.
3. Treatment Sessions
Chelation therapy begins with intravenous infusion sessions,
typically continued over several weeks to months.The frequency and total number of sessions vary depending
on your condition and treatment goals.Each infusion takes approximately 20 minutes.
4. Evaluation of Effectiveness
We assess treatment progress through tests such as
pulse wave velocity measurements to evaluate improvements
in arterial stiffness and oxidative damage.
5. Follow-Up Consultation
We review your progress and discuss whether
to continue or adjust the treatment plan.
If you have already undergone diagnostic tests for arteriosclerosis at another medical institution, are currently receiving treatment for it elsewhere, or are seeking chelation therapy for non-arteriosclerosis-related purposes, steps 2,3,and 5 may be sufficient.
Treatment Fees
At Kita-Aoyama D.CLINIC, we strive to make chelation therapy as accessible as possible for long-term care. To this end, we directly import the latest chelation formulations to help keep treatment costs reasonable. Please note that chelation therapy is not covered by public health insurance and is offered as private medical care.
| Cost per Session | Chelation Therapy (1 session): ¥11,000 (tax included) |
|---|---|
| Cost for 10 Sessions | Chelation Therapy (10 sessions): ¥99,000 (tax included) |
| Optional Tests |
Carotid Artery Pulse Wave Test: ¥11,000 (tax included) CAVI Test (Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index): ¥5,500 (tax included) Oxidative Stress Test (BAP & d-ROM): ¥5,500 (tax included) |
| Duration | Approximately 15 minutes per session |
| Recommended Frequency | 10 to 30 sessions, administered once every 1 to 2 weeks, followed by maintenance therapy once every 1 to 2 months |